Perfecting the User Experience: Why UAT Matters
Want to launch a product users love? User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is crucial for ensuring your software meets real-world needs. This listicle delivers eight user acceptance testing best practices to refine your testing process and guarantee a successful launch. Learn how to define clear test criteria, involve real users, create realistic scenarios, and more. Follow these essential steps to improve product quality, reduce costly post-launch fixes, and boost user satisfaction.
1. Define Clear Test Criteria and Success Metrics
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final gatekeeper before your product goes live. It’s the moment of truth where real users evaluate whether your software meets their needs and expectations. But without a clear roadmap, UAT can quickly become a chaotic and unproductive exercise. The cornerstone of successful UAT lies in defining crystal-clear test criteria and success metrics before testing begins. This crucial first step ensures everyone is on the same page and sets the stage for a smooth and efficient UAT process. By establishing a shared understanding of what constitutes a successful outcome, you empower your testing team to deliver actionable feedback and ensure the final product aligns perfectly with business objectives.

Defining clear criteria means outlining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) conditions that must be met for the system to be considered ready for launch. These criteria should encompass various aspects of the product, including functionality, performance, usability, and security. For instance, a specific criterion might be “Users must be able to successfully complete a purchase within three clicks.” This is measurable, achievable, relevant to the core functionality of an e-commerce platform, and can be easily tested within a specific timeframe.
This approach translates business requirements into tangible, testable elements. Think of it as creating a checklist for your product's success. This checklist includes not just functional requirements but also performance benchmarks, such as page load times or transaction processing speeds. For example, a performance benchmark might be “The application must load within two seconds on a 3G connection.” These quantifiable success metrics provide an objective evaluation framework, eliminating ambiguity and ensuring everyone understands what needs to be achieved.
Examples of successful implementations abound. When Spotify conducts UAT for its mobile app, they define specific targets, such as a 95% feature completion rate and load times under three seconds. Similarly, Bank of America’s online banking UAT incorporates specific transaction success rates, ensuring the platform’s reliability and security. Netflix, known for its personalized recommendations, uses user engagement metrics during UAT to fine-tune its algorithms and maximize user satisfaction. These companies demonstrate how clearly defined criteria and metrics drive effective UAT and ultimately contribute to product success.
Here are some actionable tips to effectively define UAT criteria and metrics:
- Involve End-Users: Get real users involved early in the criteria definition process. Their firsthand insights into their needs and workflows are invaluable.
- Use INVEST Principles: Apply the INVEST (Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Small, Testable) principles to craft robust and actionable acceptance criteria.
- Create Measurable KPIs: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that directly correlate with each business objective. This provides a clear picture of how the system contributes to overall business goals.
- Document Everything: Maintain a centralized, accessible repository for all criteria, metrics, and related documentation. This ensures transparency and facilitates collaboration among stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Validation: Before commencing UAT, review and validate the defined criteria with all stakeholders to ensure complete alignment and buy-in.
While establishing clear criteria is invaluable, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential downsides. Upfront planning can be time-intensive, and rigid criteria may inadvertently overlook valuable user feedback. There’s also the risk of missing edge cases not initially considered. However, the benefits of a well-defined UAT strategy far outweigh these potential drawbacks.
Defining clear test criteria and success metrics for UAT is not merely a best practice – it's a necessity. By investing the time and effort upfront, you ensure a more efficient and effective UAT process, leading to a higher quality product that meets user needs and drives business success. This approach, popularized by organizations like the Agile Alliance, Mike Cohn, and the ISTQB, is a testament to its efficacy in delivering exceptional software. This method deserves its place at the top of the UAT best practices list because it provides a foundational framework that guides the entire testing process and ensures a successful product launch.
2. Involve Real End Users Throughout the Process
One of the most crucial user acceptance testing (UAT) best practices is involving real end-users throughout the entire process. This means engaging the actual individuals who will use the system in its live environment, rather than relying on internal team members or proxies to stand in for them. Why? Because real users interact with software differently than internal teams. They bring unique perspectives, workflows, and expectations that can’t be replicated in a simulated environment. This practice ensures that the testing accurately reflects genuine user behavior, needs, and workflows, resulting in more realistic and valuable feedback about the system's usability and functionality. By prioritizing authentic user interaction, you significantly increase the chances of delivering a product that truly meets user needs and drives successful adoption. This elevates UAT from a mere checklist item to a powerful tool for product improvement and market success.

This approach necessitates incorporating a representative sample of your target user demographics, encompassing varied skill levels and experience. Testing scenarios should mirror real-world usage, and diverse user personas should be actively involved. Continuous user involvement, from the initial planning stages to the final execution of UAT, is essential for capturing comprehensive feedback and making informed decisions. This comprehensive involvement allows you to unearth usability issues, identify potential pain points, and validate actual user workflows – aspects that are often missed by internal technical teams. Involving users early and often also fosters a sense of ownership, leading to increased user buy-in and smoother adoption upon release.
The benefits of including real users are numerous. You gain authentic user feedback and insights directly from the source, allowing you to identify usability issues that might be missed by technical teams focused on functionality. This direct feedback validates actual user workflows, ensuring the system aligns with how users will interact with it in practice. Moreover, early user involvement cultivates a sense of ownership and increases user buy-in, leading to smoother adoption and potentially reducing training and support costs down the line. By addressing user concerns proactively during the UAT phase, you can minimize the need for extensive post-release support and troubleshooting.
However, incorporating real users in UAT also presents some challenges. Scheduling can be difficult, particularly with external users who have other commitments. Confidentiality concerns might arise, necessitating careful management of sensitive information. Users may lack technical testing knowledge, requiring clear and concise instructions. Coordinating the logistics of user participation can be time and resource intensive. Finally, be mindful of potential bias from user preferences, and strive for a balanced representation of your target audience.
Successful examples of incorporating real users abound. Microsoft's Windows 10 Insider Program, with millions of real users testing pre-release versions, exemplifies the power of large-scale user involvement. Airbnb utilizes host and guest panels to test new booking features, ensuring that changes resonate with both sides of their platform. Salesforce leverages customer advisory boards to participate in UAT for major releases, gaining valuable insights from key stakeholders. These examples highlight the value of prioritizing the user perspective in the development process.
To effectively implement this crucial best practice, consider the following tips. Recruit users who accurately match your target demographics to ensure representative feedback. Provide clear and concise instructions without being overly prescriptive, allowing users to explore the system naturally. Offer incentives for participation to encourage engagement and acknowledge their valuable contribution. Create comfortable, pressure-free testing environments where users feel empowered to provide honest feedback. Finally, document user feedback in their own words to preserve the authenticity of their experiences. Learn more about Involve Real End Users Throughout the Process as it relates to team collaboration.
By integrating real end-users into your UAT process, you’re not just testing a product; you’re building a relationship with your future users. You're demonstrating a commitment to their needs and ensuring that the final product is not only functional but also genuinely user-friendly and valuable. This commitment to user-centric design pays dividends in terms of user satisfaction, product adoption, and ultimately, business success. In the competitive landscape of today’s market, embracing this user acceptance testing best practice is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
3. Create Realistic Test Scenarios and Data
One of the most crucial user acceptance testing (UAT) best practices is creating realistic test scenarios and data. This practice ensures that your system functions as expected under real-world conditions before it goes live, minimizing the risk of post-launch issues and maximizing user satisfaction. Simply put, if your UAT doesn't accurately reflect real-world usage, how can you be confident in its results? By mirroring real-world conditions, you can identify hidden problems that might not surface in more abstract testing environments and validate the system's robustness against actual user behavior. This approach is paramount for building a reliable and user-friendly product, making it a cornerstone of effective user acceptance testing best practices.
This method involves developing test cases that mimic typical user journeys and employing production-like data sets. This means considering realistic data volumes, the complexity of user interactions, and the diversity of business scenarios users encounter daily. Imagine, for instance, an e-commerce platform: testing with just a handful of products and simple transactions won't reveal how the system performs during peak shopping seasons with thousands of concurrent users and complex order combinations. This practice is essential for any software seeking to demonstrate its readiness for real-world deployment.
Several key features contribute to the effectiveness of realistic test scenarios and data:
- Production-equivalent data volumes: Testing with data volumes comparable to production helps identify potential performance bottlenecks and scaling issues before they impact real users.
- Realistic business workflows: Mapping out and testing complete business processes, from start to finish, ensures that the system supports all user needs and that different parts of the system integrate seamlessly.
- Edge cases and exception scenarios: While focusing on typical user journeys is important, don't forget to include less common scenarios, errors, and boundary conditions. These can often reveal critical vulnerabilities.
- Data privacy and security compliance: When dealing with sensitive data, employing proper anonymization and masking techniques is paramount for adhering to regulatory requirements and protecting user privacy.
- End-to-end process coverage: Test the entire user journey across different modules and systems to identify any integration or communication issues.
Implementing this best practice offers several compelling advantages:
- Identifies performance issues under realistic conditions: Uncover bottlenecks and optimize performance before launch.
- Validates system behavior with actual data patterns: Ensures the system can handle real-world data complexities and variations.
- Tests complete business processes: Provides a comprehensive validation of the entire user journey.
- Reveals integration issues: Highlights problems arising from interactions between different system components.
- Builds confidence in production readiness: Provides stakeholders with assurance that the system is ready for real-world use.
However, there are also some challenges to consider:
- Complex data preparation and management: Creating and maintaining realistic datasets can be resource-intensive.
- Potential data privacy and security risks: Handling sensitive data requires careful planning and adherence to privacy regulations.
- Resource-intensive setup requirements: Simulating real-world environments can require significant infrastructure and resources.
- Time-consuming scenario development: Crafting comprehensive test scenarios that cover all aspects of user behavior can be time-consuming.
- Maintenance overhead for test data: Keeping test data up-to-date and relevant requires ongoing effort.
Numerous successful implementations demonstrate the value of realistic test scenarios and data: Amazon, for example, uses anonymized customer order data to thoroughly test its checkout processes before major shopping events. Healthcare systems utilize synthetic patient data matching real demographics to ensure accurate and reliable performance. Financial institutions often use transaction patterns from previous years for payment system UAT, verifying their ability to handle peak loads and diverse transaction types.
To successfully implement this best practice, consider the following tips:
- Use data masking techniques for sensitive information: Protect user privacy and comply with data regulations.
- Create data subsets representing various user segments: Ensure the system caters to the needs of all user groups.
- Include both typical and peak load scenarios: Test the system's performance under both normal and high-stress conditions.
- Validate data freshness and relevance regularly: Ensure test data accurately reflects real-world conditions.
- Test with incomplete or corrupted data scenarios: Prepare for unexpected data issues and ensure system robustness.
This best practice has been popularized by Test Data Management vendors like Informatica and IBM, DevOps practitioners promoting production-like environments, and data privacy advocates like the Privacy by Design framework. By embracing this user acceptance testing best practice, you significantly increase the likelihood of a successful product launch and ensure a positive user experience.
4. Implement Structured Test Planning and Documentation
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final gateway before your product or feature goes live. It's the moment of truth where real users assess whether it meets their needs and expectations. To ensure this crucial stage is effective and yields valuable insights, implementing structured test planning and documentation is paramount. This best practice ensures comprehensive testing coverage, streamlines communication, and ultimately sets your product up for success. It's a critical element of user acceptance testing best practices.
Structured planning and documentation lay the groundwork for a successful UAT phase. It involves creating a comprehensive test plan that outlines the objectives, scope, approach, resources, schedule, and deliverables for UAT. This blueprint also includes detailed test case specifications, execution procedures, and documentation standards, ensuring consistent, repeatable, and traceable testing processes. Think of it as the instruction manual for your UAT, guiding everyone involved and keeping the process on track.
This structured approach offers several key advantages. Comprehensive test plan documentation ensures all critical scenarios are considered, minimizing the risk of overlooked issues post-launch. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities eliminate confusion and ensure accountability within the testing team. Standardized reporting formats facilitate clear communication of test results and identified bugs to the development team. A traceability matrix links requirements to tests, ensuring complete coverage and facilitating efficient issue resolution. Finally, thorough documentation supports audit and compliance requirements, which is particularly vital in regulated industries.
For example, NASA's mission-critical software undergoes rigorous UAT with extensive documentation protocols to ensure flawless performance in extreme environments. Similarly, pharmaceutical companies adhere to strict regulatory compliance UAT documentation standards for drug development and approval. Large enterprise ERP implementations also rely heavily on detailed test planning frameworks to ensure seamless integration across complex systems.
Of course, structured planning and documentation also has potential drawbacks. It can introduce a high documentation overhead, requiring significant time and effort upfront. This might also lead to over-documentation, potentially hindering the agility needed to respond to changing requirements. Furthermore, maintaining extensive documentation can be a burden as requirements evolve throughout the product development lifecycle. It can also discourage valuable exploratory testing, where testers can deviate from pre-defined scripts to discover unexpected bugs.
However, these drawbacks can be effectively mitigated by employing the following tips: utilize templates and standardized formats to streamline documentation creation; strike a balance between comprehensive documentation and the need for agility; define clear entry and exit criteria for each test phase; maintain “living documents” that evolve with the requirements; and create visual test coverage maps for quick and easy understanding of testing progress.
Creating a comprehensive brief is essential for streamlining the UAT process. A well-structured brief ensures that all stakeholders are aligned on the testing objectives, scope, and deliverables. This helps to prevent misunderstandings and ensures that the testing process is efficient and effective. For a useful resource on building comprehensive briefs, take a look at this influencer brief template. Thinking about UAT in this structured, collaborative way, much like an influencer campaign, emphasizes the need for clarity and shared understanding among all participants.
When implementing this user acceptance testing best practice, consider the specific context of your project. For large-scale projects with complex requirements and multiple stakeholders, a high degree of structure is often essential. For smaller, more agile projects, a leaner approach to documentation may be more appropriate. Learn more about Implement Structured Test Planning and Documentation.
Ultimately, structured test planning and documentation is an invaluable best practice for successful UAT. By investing the time and effort upfront to define clear objectives, create detailed test cases, and establish standardized procedures, you significantly increase the likelihood of identifying and resolving critical issues before they impact your users. This meticulous approach helps ensure a smooth launch, higher user satisfaction, and a more robust product. By following these user acceptance testing best practices, you ensure a robust and reliable final product.
5. Establish Independent UAT Environment
One of the most crucial user acceptance testing best practices is establishing an independent User Acceptance Testing (UAT) environment. This dedicated testing environment mirrors your production setup as closely as possible but remains completely isolated from development, QA, and other testing activities. This isolation is key to obtaining reliable and valid test results, free from the interference and instability that can occur in shared or less controlled environments. A robust UAT environment allows your end-users to interact with the software under near-real-world conditions, providing invaluable feedback before the final release.

This best practice deserves its place on the list because it directly impacts the quality and reliability of your UAT process. Imagine testing a new e-commerce checkout feature while developers are simultaneously deploying code updates to the same database. The results would be chaotic and untrustworthy. An independent UAT environment eliminates such scenarios, providing a stable and predictable testing ground. This dedicated space allows for controlled access, stable configuration, and production-like infrastructure, all contributing to accurate and representative testing outcomes. It empowers your UAT testers to confidently validate the software's functionality, performance, and usability without external factors skewing the results.
A well-structured UAT environment boasts features like production-mirrored infrastructure and configuration, ensuring the software behaves as it would in a live setting. Strict access controls and change management procedures prevent unauthorized modifications, preserving the environment's integrity. Furthermore, robust data refresh and backup procedures ensure the testing data is relevant and readily available. These features contribute to a stable and consistent environment state, enabling reliable test result reproduction and supporting parallel testing activities, which are crucial for complex applications.
The benefits of an independent UAT environment are numerous. It eliminates interference from other testing activities, providing a consistent baseline for testing and mimicking production performance characteristics. This enables reliable test result reproduction, crucial for identifying and resolving issues effectively. Furthermore, an independent environment supports parallel testing activities, accelerating the overall UAT process. For instance, major banks maintain separate UAT environments for critical financial systems to ensure rigorous testing without disrupting ongoing operations. Similarly, e-commerce giants like eBay utilize production-mirror environments for UAT, allowing them to test new features and updates under realistic conditions before rolling them out to millions of users. Even cloud providers recognize the importance of dedicated UAT environments and offer specific services to facilitate their creation and management.
However, it's essential to acknowledge the potential drawbacks. Setting up and maintaining an independent UAT environment can incur high infrastructure and maintenance costs due to resource duplication across environments. Managing the environment’s complexity can also be challenging, requiring specialized expertise. Furthermore, there's a risk of "environment drift"—the gradual divergence of the UAT environment from the production environment over time. Finally, coordinating access and managing changes within the environment can add overhead to the testing process.
To mitigate these challenges, consider implementing the following tips: utilize environment monitoring and alerting systems to proactively identify and address issues, employ Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for consistent and repeatable environment deployments, establish clear environment refresh procedures to maintain data relevance, meticulously control and document all environment changes, and regularly validate environment-production parity to minimize drift.
By carefully weighing the pros and cons and implementing these best practices, you can leverage the power of an independent UAT environment to significantly enhance the quality, reliability, and ultimately the success of your software releases. This approach is particularly valuable for complex systems, applications with high user traffic, and projects where data integrity is paramount. Investing in a robust UAT environment is an investment in the quality of your product and the satisfaction of your users.
6. Execute Systematic Defect Management
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final gateway before your product reaches your customers. It's where real users put your software through its paces, uncovering hidden issues and providing valuable feedback. But identifying these issues is only half the battle. To truly maximize the value of UAT, you need to execute systematic defect management. This crucial best practice transforms scattered bug reports into actionable insights, ensuring a polished, high-quality product launch and ongoing success.
Systematic defect management is a structured approach to identify, document, prioritize, track, and resolve defects found during UAT. It involves implementing clear defect classification criteria, establishing escalation procedures, and defining communication protocols to ensure issues are addressed efficiently and transparently. Think of it as a well-oiled machine that takes raw defect data and transforms it into a roadmap for improvement.
Without a system in place, defects can easily slip through the cracks. Critical bugs might go unnoticed until launch, leading to frustrated users and damaging your brand reputation. A systematic approach, however, ensures no critical issue is overlooked, providing invaluable visibility into system quality and facilitating informed go/no-go decisions.
This approach boasts a range of features designed to streamline the entire defect lifecycle: standardized defect reporting templates ensure consistency; clear severity and priority classifications help focus efforts on the most impactful issues; defined escalation and resolution workflows facilitate swift action; real-time defect tracking and reporting offers continuous visibility; and integration with development and project management tools, like Atlassian’s Jira, streamlines collaboration. Companies like Spotify utilize Jira for UAT defect tracking, while enterprises often rely on ServiceNow’s IT service management for their complex workflows. Even tech giants like Google and Facebook employ custom defect management processes, emphasizing the universal importance of this practice.
While the benefits are undeniable, it's important to acknowledge the potential drawbacks. Implementing a systematic defect management process introduces administrative overhead. There's also the risk of over-classification, which can slow down progress, and the potential for a defect backlog to accumulate. Tool dependency and the associated training requirements can also be a barrier to entry. Finally, a focus on sheer defect quantity can sometimes overshadow the importance of addressing the most impactful quality issues.
So, when should you use this approach? Simply put: always. Whether you’re a solo developer, part of a small startup, or working within a large corporation, systematic defect management is essential for any product undergoing UAT. It's particularly valuable for complex projects with multiple stakeholders, where clear communication and efficient workflows are paramount. By proactively addressing defects, you not only improve product quality but also cultivate a culture of continuous improvement.
To effectively implement systematic defect management, consider these actionable tips:
- Define clear severity and priority criteria upfront: Establish a shared understanding of what constitutes a critical, major, minor, or trivial defect.
- Establish service level agreements (SLAs) for defect resolution: Set realistic expectations for how quickly different types of defects should be addressed.
- Use automation for defect routing and notifications: Streamline workflows and ensure timely communication.
- Conduct regular defect triage meetings: Bring together key stakeholders to discuss, prioritize, and assign defects.
- Track metrics like defect discovery and resolution rates: Monitor progress and identify areas for improvement. Analyze trends to refine your testing processes and prevent recurring issues.
By incorporating systematic defect management into your UAT process, you empower your team to identify, address, and learn from defects, ultimately delivering a superior product that meets and exceeds user expectations. Learn more about Execute Systematic Defect Management to further enhance your defect documentation skills. This investment in quality will pay dividends in the long run, leading to increased customer satisfaction, improved brand reputation, and ultimately, greater business success.
7. Conduct Comprehensive User Training and Preparation
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final gateway before your product launches. It’s where real users put your product through its paces in real-world scenarios. But what if those users aren’t equipped to effectively test your product? That’s where comprehensive user training and preparation comes in – a critical best practice that can make or break your UAT. This crucial step ensures your testers understand the system, the testing objectives, and their specific roles, leading to more valuable feedback and a smoother launch. Ignoring this step can lead to wasted time, missed bugs, and ultimately, a less successful product launch.
This best practice involves much more than just a quick product demo. It’s about empowering your users to become effective testers. This includes providing them with a solid understanding of the system's functionality, walking them through test cases, and offering ongoing support throughout the UAT process. Think of it as equipping your testers with the tools and knowledge they need to provide you with the most accurate and insightful feedback possible.
Features of a robust UAT training program include:
- System Functionality Overview Sessions: These sessions provide a high-level understanding of the system's features and how they work together.
- Test Case and Scenario Walkthroughs: Users learn how to execute specific test cases and understand the expected outcomes.
- Role-Specific Training Materials: Customized materials address the unique needs and responsibilities of different user groups.
- Hands-on Practice Opportunities: Users get to experiment with the system in a safe environment before formal testing begins.
- Ongoing Support and Guidance During Testing: A dedicated support channel ensures users can quickly get answers to their questions and resolve any issues.
The benefits of investing in user training are substantial:
- Improves Test Execution Quality and Efficiency: Trained users execute test cases more accurately and efficiently, saving valuable time and resources.
- Reduces User Confusion and Frustration: Clear instructions and support minimize user frustration and ensure a smoother testing process.
- Increases Meaningful Feedback Generation: Well-trained users provide more insightful and actionable feedback.
- Builds User Confidence and Engagement: Training empowers users and fosters a sense of ownership in the testing process.
- Identifies Training Needs for Production Rollout: UAT training can highlight areas where additional training may be needed for the final product launch.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Additional Time and Resource Investment: Developing and delivering training requires time and resources.
- Risk of Influencing User Behavior Through Training: Overly prescriptive training can bias user behavior and limit the discovery of genuine usability issues.
- Scheduling Challenges for Training Sessions: Coordinating training schedules with busy users can be difficult.
- Potential Information Overload for Users: Too much information at once can overwhelm users and hinder their learning.
- Training Material Creation and Maintenance Effort: Creating and maintaining up-to-date training materials requires ongoing effort.
Examples of successful UAT training implementations include Workday's customer success teams, who provide comprehensive training for HR system implementations; Oracle's structured user enablement programs for ERP UAT; and Salesforce's Trailhead platform, which offers UAT-specific training modules. These companies recognize the value of investing in user preparation and have built robust programs to support it.
To maximize the effectiveness of your UAT training, consider these tips:
- Tailor training to different user skill levels: Novice users may require more hands-on instruction, while experienced users may benefit from self-paced learning.
- Provide job aids and quick reference materials: These resources can help users quickly find answers to common questions during testing.
- Include both system navigation and business process training: Users need to understand not only how the system works but also how it fits into their daily workflows.
- Record training sessions for later reference: This allows users to review the material at their own pace and revisit key concepts as needed.
- Gather feedback on training effectiveness: Ask users for feedback on the training to identify areas for improvement.
When deciding on the most effective training format for your users, consider their skill levels and tailor the approach accordingly. The following decision tree provides a simple framework for choosing the right training format.
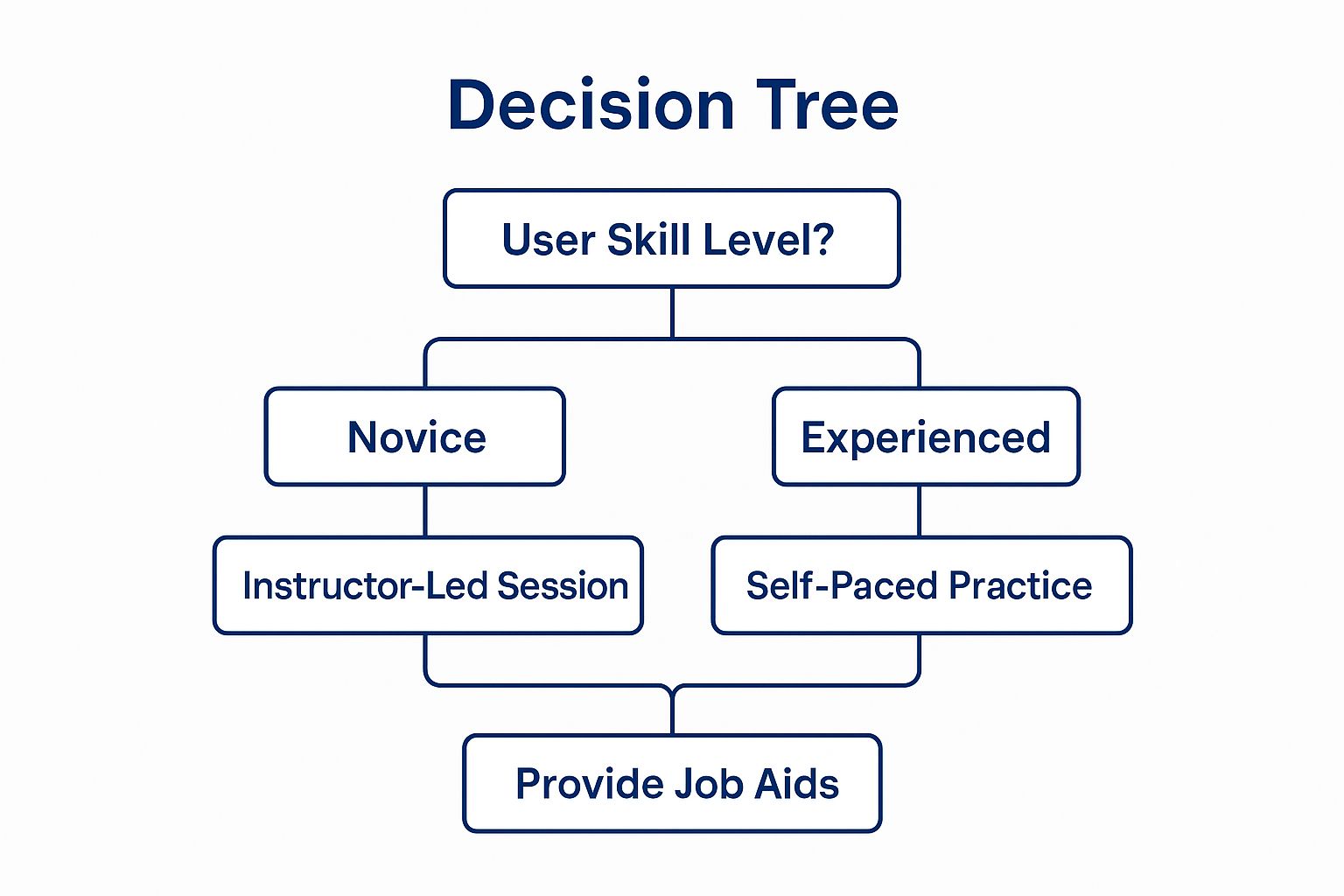
The infographic above illustrates a decision-making process for selecting the appropriate user training format based on skill level. Whether users are novices requiring instructor-led sessions or experienced individuals who thrive with self-paced practice, providing job aids is a universally beneficial supplement.
By investing in comprehensive user training and preparation, you’re not just preparing your users for UAT – you’re setting the stage for a successful product launch. You’re ensuring that your product meets the needs of your users and that they are equipped to use it effectively. This translates to a higher quality product, happier users, and ultimately, a more successful business.
8. Plan Strategic Go-Live Decision Framework
A robust User Acceptance Testing (UAT) phase is crucial for ensuring software quality and user satisfaction. However, even the most thorough UAT is useless without a clear and strategic go-live decision framework. This critical component of user acceptance testing best practices determines whether your software is truly ready for deployment or requires further refinement. A well-defined go-live decision framework establishes a structured process for evaluating UAT results against pre-determined criteria, minimizing deployment risks and instilling confidence in all stakeholders. This isn't just about ticking boxes; it's about making informed, objective decisions that protect your investment and reputation.
This framework operates on the principle of objective evaluation. It moves beyond gut feelings and anecdotal evidence, instead relying on quantifiable data and predefined metrics. Before UAT even begins, specific criteria for success are established. These might include the percentage of test cases passed, the severity and frequency of identified bugs, and the overall user satisfaction score. As the UAT progresses, the results are meticulously documented and compared against these established benchmarks.
The go-live decision framework incorporates a multi-tiered approach involving key stakeholders. Product owners, developers, quality assurance teams, and business representatives all play a crucial role in assessing the system's readiness. A formal sign-off process ensures everyone is aligned and accountable. This collaborative process fosters transparency and builds consensus, paving the way for a smooth and confident launch.
The process also integrates risk assessment and mitigation strategies. Potential issues and challenges are identified early on, and contingency plans are developed to address them. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of unforeseen problems, allowing for swift and effective solutions should they arise. Rollback procedures are also defined, providing a safety net in case critical issues surface post-deployment.
Communication and notification protocols are essential elements of a robust go-live decision framework. Regular updates are shared with all stakeholders, keeping everyone informed about the progress of UAT and any potential roadblocks. This transparent communication fosters trust and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
The benefits of implementing a strategic go-live decision framework are manifold. It ensures objective deployment decisions based on data, minimizing the risk of impulsive or emotionally-driven choices. This reduces the likelihood of unpleasant surprises post-deployment and strengthens stakeholder confidence in the system's stability and performance. A documented decision-making process also supports audit trails and compliance requirements, which is crucial in regulated industries.
Examples of successful implementation of such frameworks abound. NASA's meticulous mission readiness reviews for space systems highlight the importance of rigorous pre-launch evaluations. Similarly, the stringent regulatory approval processes in the financial services sector for trading systems underscore the need for robust risk assessment and mitigation strategies. Healthcare organizations, with their focus on patient safety, employ rigorous reviews for clinical systems, demonstrating the critical role of a well-defined go-live decision framework.
While implementing a go-live decision framework offers significant advantages, it's essential to be aware of potential drawbacks. Strict adherence to criteria might delay deployment for seemingly minor issues. Furthermore, the involvement of multiple stakeholders can sometimes lead to complex decision-making processes and even analysis paralysis. Navigating these complexities requires strong leadership and a commitment to collaborative problem-solving.
Here are some practical tips for implementing an effective go-live decision framework:
- Define decision criteria with measurable thresholds: Avoid vague criteria. Use concrete metrics, such as "95% of test cases passed" or "no critical bugs identified."
- Establish clear roles and authority levels: Define who has the final say in go/no-go decisions and how disagreements are resolved.
- Create decision templates and checklists: Standardize the decision-making process to ensure consistency and thoroughness.
- Plan for phased or gradual rollout options: Minimize risk by deploying the system to a limited group of users before a full-scale launch.
- Document rationale for all go/no-go decisions: Create a clear audit trail for future reference and analysis.
By adopting these user acceptance testing best practices, you can ensure a smoother, more predictable, and ultimately more successful software launch. This strategic approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters confidence among stakeholders, paving the way for a positive user experience. Methodologies like the Project Management Institute (PMI)'s framework, Robert Cooper's Stage-Gate innovation process, and ITIL service transition best practices further emphasize the importance of a structured go-live decision process. Investing in a comprehensive go-live decision framework is an investment in the long-term success of your software project.
UAT Best Practices Comparison
| Best Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Define Clear Test Criteria and Success Metrics | Medium – requires detailed upfront planning 🔄 | Moderate – stakeholder coordination needed ⚡ | Objective evaluation, faster decisions, fewer issues 📊 | Projects needing clear business alignment and measurable goals 💡 | Eliminates ambiguity, aligns with business goals ⭐ |
| Involve Real End Users Throughout the Process | High – coordination with external users 🔄 | High – managing diverse user groups ⚡ | Authentic feedback, usability validation, increased adoption 📊 | User-centric apps, highly interactive systems 💡 | Real-world insights, better user acceptance ⭐ |
| Create Realistic Test Scenarios and Data | High – complex data prep and scenario design 🔄 | High – data management and compliance ⚡ | Performance validation, integration issue detection 📊 | Systems with complex workflows and large data volumes 💡 | Tests realistic use, uncovers hidden issues ⭐ |
| Implement Structured Test Planning and Documentation | Medium-High – extensive documentation needed 🔄 | Moderate – ongoing document maintenance ⚡ | Consistent test execution, compliance support 📊 | Regulated industries, large projects requiring audit trails 💡 | Ensures coverage, repeatability, audit readiness ⭐ |
| Establish Independent UAT Environment | High – setup and maintenance of separate systems 🔄 | High – infrastructure and monitoring ⚡ | Reliable, reproducible tests; environment stability 📊 | Critical systems needing isolated test environments 💡 | Eliminates interference, mimics production conditions ⭐ |
| Execute Systematic Defect Management | Medium – process definition and tool usage 🔄 | Moderate – tool integration and training ⚡ | Clear defect visibility, informed deployment decisions 📊 | Projects with complex defect tracking needs 💡 | Ensures issue prioritization, clear communication ⭐ |
| Conduct Comprehensive User Training and Preparation | Medium – training materials and sessions 🔄 | Moderate – scheduling and resource allocation ⚡ | Higher test quality, user confidence, better feedback 📊 | Projects with non-technical users or new systems 💡 | Reduces confusion, increases engagement ⭐ |
| Plan Strategic Go-Live Decision Framework | Medium – stakeholder coordination and planning 🔄 | Moderate – governance and documentation ⚡ | Objective deployment decisions, risk mitigation 📊 | Highly regulated or mission-critical deployments 💡 | Clear accountability, reduces surprises ⭐ |
Ready to Launch? UAT Best Practices in Action
Implementing user acceptance testing best practices is crucial for any successful product launch. From defining clear test criteria and success metrics to establishing an independent UAT environment and managing defects systematically, each step plays a vital role. Remember, involving real end-users and creating realistic test scenarios are cornerstones of effective user acceptance testing best practices. By prioritizing these user acceptance testing best practices, you’ll gain invaluable insights into user behavior, ensuring a smoother launch and higher user satisfaction. This ultimately translates to reduced post-release headaches, a faster time to market, and a significantly higher return on investment. Mastering these concepts empowers your team to deliver exceptional user experiences, fostering positive word-of-mouth and driving long-term product success.
By focusing on thorough planning, realistic testing, and structured feedback, you can confidently release a product that truly meets user needs and exceeds expectations. Don't let your hard work go to waste by skipping crucial UAT steps. Streamline your UAT process and gather invaluable user feedback with BugSmash. Visit BugSmash to learn how this intuitive platform can help you implement these user acceptance testing best practices and ensure a flawless product launch.


![Read more about the article What Is Image Annotation & How Does It Work? [2025 Guide for UX Teams & Developers]](https://bugsmash.io/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/thumbnail-19-768x432.jpg)

