Unlocking the Power of UX: 7 Testing Methods You Need to Know
Want to create digital experiences that convert? Mastering user experience (UX) is key. This listicle reveals seven essential user experience testing methods to boost your product's usability and drive results. Learn how usability testing, A/B testing, user interviews, eye tracking, card sorting, surveys, and heatmaps/session recordings can provide invaluable user insights. We'll also explore how tools like BugSmash can streamline your feedback process, maximizing the impact of these testing methods. Let's dive in.
1. Usability Testing
Usability testing is a cornerstone of effective user experience (UX) testing methods, allowing you to evaluate how easily users interact with your product and complete specific tasks. This method involves observing users as they engage with your product or service, typically in a controlled environment, to identify pain points, areas for improvement, and ultimately, enhance user satisfaction. Participants are given specific tasks to complete, while observers meticulously watch, listen, and take notes, capturing valuable qualitative and quantitative data. This provides invaluable insights into the user's thought process and behavior, revealing usability issues that may not be apparent to designers or developers.
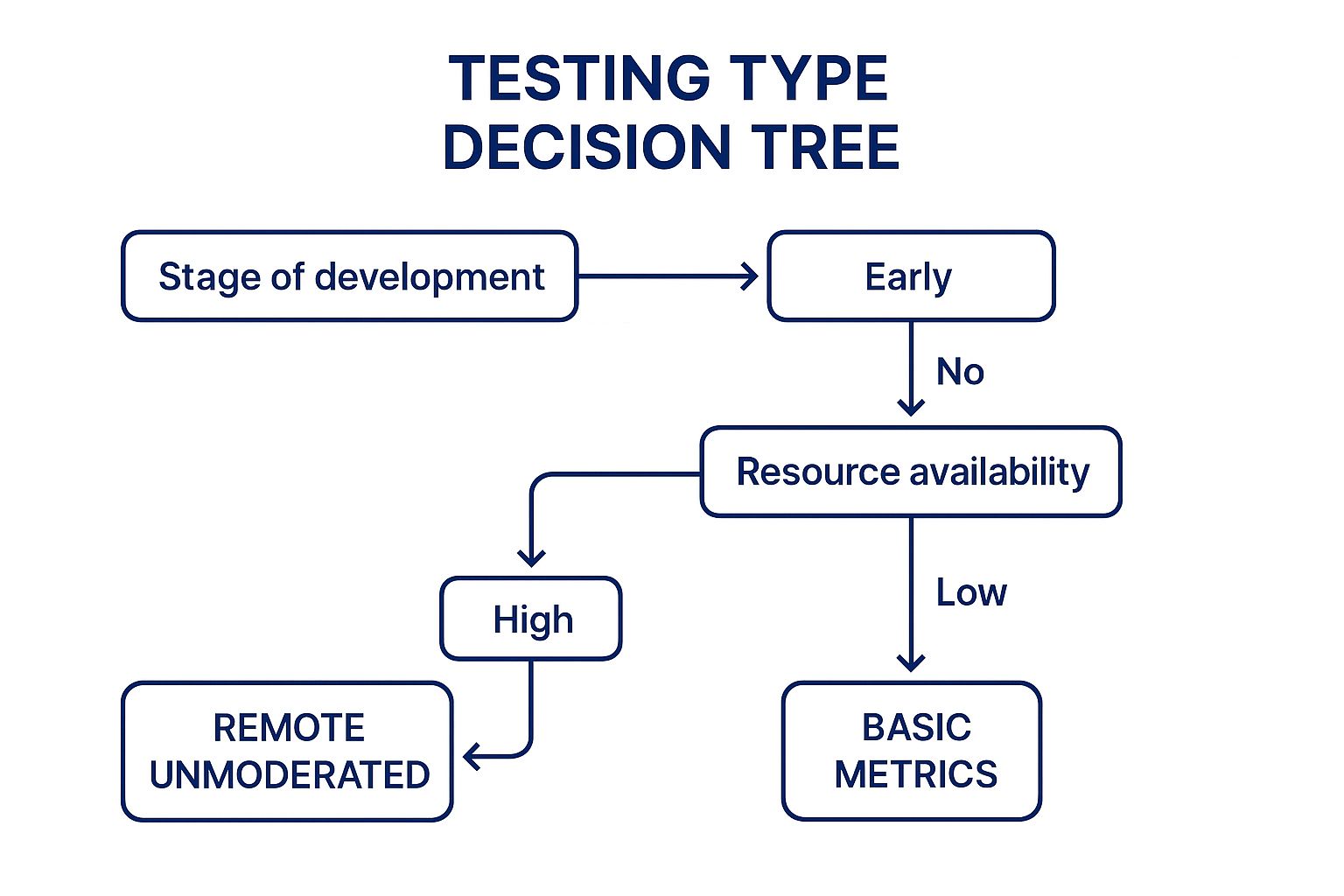
The infographic above provides a decision tree to guide you through selecting the right type of usability testing. It visualizes the key decision points in choosing between moderated and unmoderated usability testing, starting with whether you need in-depth qualitative data.
From industry giants like Google, Apple, Netflix, and Airbnb, usability testing has proven its worth in optimizing products and driving user engagement. Google's HEART framework implementation, Apple's dedicated usability labs, Netflix's iterative testing for UI changes, and Airbnb's focus on optimizing booking flows are testaments to the power of this method. These examples demonstrate how usability testing can be employed across various product development stages, from initial design to post-launch refinement, proving its versatility and importance for anyone aiming to create user-centered products.
Usability testing offers a range of features tailored to gather diverse insights. Moderated sessions provide real-time interaction and probing, while unmoderated sessions offer flexibility and scalability. Task-based scenarios ensure users interact with the product in a realistic context, revealing how they achieve specific goals. Implementing the "think-aloud" protocol uncovers users' cognitive processes, providing valuable insight into their decision-making. Furthermore, collecting performance metrics like time-on-task, success rate, and error rate allows you to quantify usability issues and track improvements over time.
When and Why to Use Usability Testing:
Usability testing is invaluable throughout the product development lifecycle. Use it during early prototyping to validate design concepts, during development to identify and fix usability issues, and post-launch to continuously optimize the user experience. This iterative approach ensures a user-centered design process, resulting in a product that truly resonates with your target audience.
Pros:
- Provides direct insights into how real users interact with your product.
- Identifies usability problems that might be overlooked by designers.
- Offers both behavioral and attitudinal data, providing a holistic understanding of the user experience.
- Can be conducted at various stages of product development.
- Relatively easy to implement with proper planning.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Lab settings may create artificial behaviors.
- Sample sizes are often small, potentially limiting statistical significance.
- Requires skilled facilitators to avoid bias.
- May not fully capture real-world usage patterns.
Actionable Tips for Effective Usability Testing:
- Define clear, realistic tasks: Ensure tasks represent actual user goals and are easily understood by participants.
- Recruit participants who closely match your target audience: This ensures the feedback you receive is relevant and actionable.
- Maintain a neutral stance to avoid biasing participants: Encourage open and honest feedback without leading participants towards specific answers.
- Focus on patterns rather than individual opinions: Look for recurring issues across multiple participants to identify significant usability problems.
- Test early and often throughout the development process: Integrating usability testing into your workflow allows for iterative improvements and prevents costly redesigns later on.
- Combine with other user experience testing methods for a complete picture: Usability testing is most effective when used in conjunction with other research methods, providing a comprehensive understanding of the user experience.
The decision tree in the infographic simplifies the decision-making process for choosing between moderated and unmoderated usability testing, helping you tailor your approach to your specific needs and resources. For instance, if you need to understand the "why" behind user behavior, moderated testing is the preferred route. If budget is a constraint and you need quick feedback, unmoderated testing could be a better fit.
Learn more about Usability Testing
Usability testing deserves its place as a leading user experience testing method because it offers direct, actionable insights into user behavior. By observing real users interacting with your product, you can identify and address critical usability issues, resulting in a more user-friendly and ultimately, more successful product. This method is a powerful tool for anyone involved in creating digital products, from individual creators to large organizations, empowering them to build products that truly meet the needs of their users.
2. A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a cornerstone of user experience (UX) testing methods. It's a powerful way to optimize your digital products and marketing campaigns by letting your users guide your decisions. This data-driven approach involves comparing two versions (A and B) of a webpage, app feature, or other digital element, presented to different user segments. By analyzing how each version performs against specific metrics, you can pinpoint which resonates more effectively with your audience, leading to improved conversion rates, engagement, and ultimately, a superior user experience. This method removes guesswork and allows for evidence-based decision-making, crucial for anyone looking to create truly user-centric experiences.

A/B testing leverages controlled experiments with randomized user assignment, ensuring unbiased results. Statistical analysis reveals significant performance differences between the variations. You define specific success metrics (e.g., conversion rates, click-through rates, bounce rates) tailored to your goals. This allows you to isolate specific variables, like headline text, button color, or image placement, and measure their impact. The flexibility of A/B testing empowers you to run multiple tests concurrently, accelerating the optimization process.
Why A/B Testing Deserves its Place in the List: A/B testing provides quantifiable evidence to support design and marketing choices. It minimizes risk by validating changes with real users before full implementation, preventing costly mistakes. The method's sensitivity allows detection of even subtle performance variations, unveiling optimization opportunities often overlooked. Furthermore, it scales effortlessly to large user bases and remains relatively cost-effective compared to other UX testing methods.
Features and Benefits:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Base your choices on user behavior, not assumptions.
- Risk Mitigation: Validate changes before a full rollout to minimize potential negative impact.
- Granular Insights: Isolate and test specific variables for maximum clarity.
- Scalability: Easily test with large user groups for statistically significant results.
- Cost-Effectiveness: A relatively inexpensive way to gather valuable user data.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Provides quantitative data, reduces risk, detects subtle differences, scalable, cost-effective.
- Cons: Only tests existing elements, requires sufficient traffic, can be time-consuming, doesn't always reveal "why," multiple tests can create interaction effects.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Amazon: Constantly optimizes product pages and checkout flow through A/B testing.
- Booking.com: Known for its culture of running hundreds of concurrent A/B tests.
- Netflix: Tests thumbnail images to maximize viewer engagement.
- Obama's 2012 Presidential Campaign: Raised an additional $60 million through A/B testing on their donation page.
Actionable Tips for Effective A/B Testing:
- Isolate Variables: Test one variable at a time to understand its impact clearly.
- Sample Size: Calculate the required sample size for statistically significant results beforehand.
- Test Duration: Run tests long enough to capture variations due to time of day or week.
- Predefined Metrics: Clearly define your success metrics before starting the test.
- Segment Analysis: Analyze results by user segment, not just overall performance.
- Qualitative Follow-up: Pair A/B testing with qualitative research (e.g., user interviews) to uncover the "why" behind the results.
When and Why to Use A/B Testing:
Use A/B testing when you need to make data-backed decisions regarding any aspect of the user experience, from website design and app interfaces to marketing copy and email campaigns. This approach is invaluable for optimizing conversions, increasing engagement, and improving overall user satisfaction. Whether you're a product manager, marketer, or founder, A/B testing is a critical tool for building truly user-centric digital experiences.
Popularized By: Ron Kohavi (Microsoft), Optimizely, Google Optimize, VWO (Visual Website Optimizer)
This method empowers product teams, individual creators, marketing teams, quality analysts, developers, product marketing managers, product managers, founders, digital agencies, and content creators to make data-driven decisions and optimize user experiences. A/B testing is an essential component of any user experience testing strategy, allowing you to continuously improve and refine your digital offerings based on real user behavior.
3. User Interviews: Uncover the "Why" Behind User Behavior
User interviews are a cornerstone of effective user experience (UX) testing methods. They provide invaluable qualitative data that goes beyond the "what" and delves into the "why" behind user behavior. This method involves structured conversations with users or potential users to gather insights about their needs, behaviors, preferences, and pain points. If you truly want to understand your users and build products that resonate, incorporating user interviews into your UX testing arsenal is essential.
How User Interviews Work:
User interviews are typically one-on-one sessions, conducted either in person or remotely, where a researcher engages with a participant using a semi-structured or structured interview guide. This guide ensures key topics are covered, while also allowing for flexibility to explore interesting tangents and unexpected insights. The interviewer uses open-ended and probing questions to encourage detailed responses and understand the user's perspective. These sessions are usually 30-60 minutes long and are often audio/video recorded for later analysis.
Why User Interviews Deserve a Place in Your UX Toolkit:
User interviews provide a level of rich, detailed qualitative insight that other UX testing methods simply can't match. They allow researchers to:
- Deeply explore user motivations: Go beyond surface-level observations and understand the underlying reasons driving user behavior.
- Build empathy with users: Stepping into the user's shoes allows you to develop a deeper understanding of their needs and challenges.
- Uncover unexpected insights and use cases: Open-ended questions can reveal surprising ways users interact with your product or service, leading to valuable innovations.
- Validate or invalidate assumptions: Challenge your assumptions about user behavior and ensure you're building a product that truly meets their needs.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Numerous companies have leveraged user interviews to drive product development and improve user experience. For instance:
- Spotify: User interviews played a crucial role in informing the development and refinement of their personalized playlist features.
- Slack: Interview-based research helped Slack understand the nuances of enterprise collaboration and tailor their platform accordingly.
- Intuit: Regular customer interviews are integral to Intuit's ongoing improvement of TurboTax, ensuring it remains user-friendly and addresses evolving tax regulations.
Pros and Cons:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides rich, detailed qualitative insights | Time-intensive to conduct and analyze |
| Allows for follow-up questions and clarification | Subject to recall bias and self-reporting inaccuracies |
| Builds empathy with users | Requires skilled interviewers to avoid leading questions |
| Flexible format adaptable to research needs | Small sample sizes limit generalizability |
| Can uncover unexpected insights and use cases | What people say often differs from what they actually do |
Actionable Tips for Conducting Effective User Interviews:
- Create a discussion guide but remain flexible: Prepare a list of key questions, but allow room for spontaneous exploration.
- Start with general questions before moving to specifics: Ease participants into the conversation and build rapport.
- Use the "five whys" technique to dig deeper into motivations: Uncover the root causes behind user behaviors and preferences.
- Avoid leading questions that suggest preferred answers: Maintain objectivity and encourage honest responses.
- Conduct interviews in pairs: One person leads the discussion while the other takes notes and observes body language.
- Schedule analysis time immediately after interviews while fresh: Capture key takeaways and insights before they fade.
When and Why to Use User Interviews:
User interviews are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Early-stage product development: Understanding user needs and pain points before building.
- Identifying usability issues: Uncovering problems users encounter while interacting with a product or service.
- Gathering feedback on new features: Evaluating user reactions and identifying areas for improvement.
- Exploring user motivations and behaviors: Gaining a deeper understanding of the "why" behind user actions.
Popularized By:
The practice of user interviews has been championed by UX thought leaders like Steve Portigal and Erika Hall, as well as organizations like IDEO and Spotify's research team.
By incorporating user interviews into your user experience testing methods, you can gather invaluable insights that inform product development, improve usability, and ultimately create a better experience for your users.
4. Eye Tracking
Eye tracking is a powerful user experience (UX) testing method that provides objective, data-driven insights into how users visually interact with your product, website, or other digital interface. It goes beyond what users say they do and reveals what they actually do by precisely measuring where they look, for how long, and in what order. This allows you to understand visual attention, cognitive processing, and user behavior at a granular level, unlocking a deeper understanding of the user experience. By leveraging eye tracking as one of your user experience testing methods, you can pinpoint usability issues, optimize designs for maximum impact, and ultimately create more user-centered products.

Eye tracking uses specialized hardware and software to track eye movements and fixations. This technology generates a wealth of valuable data, including: heat maps visualizing areas of high visual concentration; gaze plots illustrating the sequence of eye movements; fixation duration and frequency metrics indicating points of interest and potential confusion; saccade (rapid eye movement) analysis revealing visual search patterns; and Areas of Interest (AOI) performance comparisons for evaluating the effectiveness of different design elements.
Why Eye Tracking Deserves Its Place in Your UX Testing Arsenal:
Eye tracking provides a unique window into the user's subconscious visual processing, uncovering insights that traditional user experience testing methods like surveys and user interviews often miss. Users might not be consciously aware of why they struggle with a particular interface element, or they might misremember their interaction. Eye tracking eliminates this ambiguity, offering concrete visual evidence of user behavior. This objective data is invaluable for identifying overlooked or distracting elements, comparing design alternatives, and optimizing user flows. The highly visual results – heatmaps and gaze plots – are also easy for stakeholders to grasp, facilitating communication and buy-in for design changes.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Industry giants like Google, Facebook, Airbnb, and The New York Times have successfully integrated eye tracking into their UX testing processes. Google utilizes eye tracking to refine search results page layouts, while Facebook leverages the technique to optimize newsfeed engagement. Airbnb has improved listing page designs based on eye tracking data, and The New York Times has used it to optimize article layout for better readability. These examples demonstrate the wide applicability and tangible benefits of eye tracking across diverse digital platforms.
Pros & Cons of Eye Tracking:
Pros:
- Provides objective data about visual behavior
- Reveals unconscious viewing patterns users can't self-report
- Helps identify overlooked or distracting elements
- Useful for comparing design alternatives
- Highly visual results that stakeholders can easily understand
Cons:
- Specialized equipment can be expensive
- Setup and calibration can be time-consuming
- Requires technical expertise for proper implementation
- May create artificial viewing behavior in lab settings
- Looking at something doesn't necessarily indicate comprehension
Actionable Tips for Effective Eye Tracking:
- Combine with think-aloud protocols: Gain context on why users look where they do by having them verbalize their thoughts during the eye tracking session.
- Use realistic tasks and content: Avoid placeholder text and ensure users interact with real-world scenarios.
- Account for cultural reading patterns: Consider left-to-right vs. right-to-left reading patterns when analyzing data.
- Run pilot tests: Refine your study protocols and ensure accurate data collection.
- Consider remote eye tracking: Explore remote eye tracking solutions for more natural user environments.
- Define clear areas of interest (AOIs) before analysis: Focus your analysis and derive meaningful insights.
Popularized By: Tobii Technology, Nielsen Norman Group, Baxter and Courage (authors of 'Understanding Your Users'), EyeQuant.
By incorporating eye tracking into your UX testing toolkit, you gain a competitive edge in understanding user behavior and creating truly user-centered designs. This method empowers you to make data-driven decisions, optimize user interfaces, and ultimately deliver exceptional digital experiences.
5. Card Sorting: Uncover How Users Think
Card sorting is a powerful, yet surprisingly simple, user experience testing method that deserves a prominent place in any UX researcher's toolkit. This technique allows you to peek inside the minds of your users and understand how they naturally categorize information. By having participants organize content items into groups, you gain invaluable insights into their mental models, which are crucial for creating intuitive and user-friendly experiences. This directly translates into improved information architecture, more effective navigation systems, and a better overall user experience. Whether you're a product manager, developer, content creator, or part of a marketing agency, understanding how card sorting works can significantly elevate your work.
How Card Sorting Works:
Imagine handing a user a stack of cards, each labeled with a topic or content item from your website or app. You then ask them to sort these cards into groups that make logical sense to them. This process reveals how users perceive the relationships between different pieces of information, highlighting potential gaps in your current structure and areas for improvement.
Card sorting comes in three main flavors:
- Open Card Sorting: Users create their own categories and label them, providing rich qualitative data and revealing how users conceptualize your content.
- Closed Card Sorting: Users sort items into predefined categories, useful for validating existing structures or comparing user understanding with your intended organization.
- Hybrid Card Sorting: This approach combines the benefits of both open and closed sorting, allowing users to sort into predefined categories while also offering the flexibility to create new ones.
These sessions can be conducted individually or in groups, and can be implemented in-person or remotely using online tools like OptimalSort.
Why Use Card Sorting?
Card sorting offers a unique blend of qualitative and quantitative data, making it a versatile tool for a variety of UX challenges. It's particularly effective for:
- Informing Information Architecture: Design intuitive sitemaps and navigation structures that align with user expectations.
- Optimizing Menu Structures: Create menus that are easy to understand and navigate.
- Improving Content Organization: Group related content in a way that makes sense to your users.
- Identifying Confusing Terminology: Uncover terms that users misinterpret or don't understand.
Real-World Success Stories:
Major companies like IBM, Salesforce, REI, and Adobe have leveraged card sorting to improve their user experience. For example, IBM used card sorting to restructure their developer documentation, resulting in a more user-friendly and accessible resource. Salesforce employed this technique to reorganize their CRM menu, leading to increased user efficiency and satisfaction.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Directly incorporates user perspectives
- Relatively inexpensive and quick to implement
- Easily scales through remote testing tools
- Provides both qualitative and quantitative data
- Helps identify confusing terminology or content
Cons:
- Results can be difficult to analyze with large item sets
- Participants may group by different criteria (task vs. topic)
- May not account for context of use or user journeys
- Can be challenging to reconcile conflicting sorting patterns
- Results represent organization preferences, not usage patterns
Actionable Tips for Effective Card Sorting:
- Limit the number of cards: 30-50 is typically manageable.
- Use clear, jargon-free language on cards: Ensure participants understand the terms.
- Ask participants to think aloud during the sorting process: Gain valuable insights into their reasoning.
- Run a pilot test: Refine card content and instructions.
- Consider tree testing as a complementary validation method: Test the effectiveness of your resulting information architecture.
- Use specialized tools for more efficient analysis: Tools like OptimalSort can streamline the process.
By incorporating card sorting into your UX testing process, you can create digital experiences that truly resonate with your target audience, leading to increased engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, success.
6. Surveys and Questionnaires: Tap into the Voice of Your Users
Surveys and questionnaires are a powerful user experience testing method, providing a direct line to the thoughts and feelings of your target audience. As a cornerstone of UX research, they offer a structured and scalable approach to gathering invaluable feedback, enabling you to make data-driven decisions that enhance user satisfaction and drive product success. This method deserves its place on this list due to its versatility, reach, and ability to provide both broad overviews and specific insights into the user experience.
This method involves presenting users with a pre-determined set of questions designed to elicit information about their demographics, behaviors, preferences, satisfaction levels, and overall attitudes toward your product or experience. These questions can take various forms, from multiple-choice and Likert scales (e.g., rating agreement on a scale of 1 to 5) to open-ended questions encouraging more detailed responses. Branching logic can further personalize the survey experience, tailoring subsequent questions based on previous answers. This adaptability makes surveys and questionnaires suitable for a wide range of UX research goals.
Features and Benefits:
- Standardized Question Formats: Ensures consistency and comparability of responses.
- Branching Logic: Creates a more personalized and engaging survey experience.
- Large Sample Capabilities: Allows for statistically significant insights and generalization to the broader user base.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection: Captures both measurable data and rich, descriptive feedback.
- Various Distribution Methods: Reach users through email, website intercepts, in-app prompts, and more.
Why Use Surveys and Questionnaires?
This approach is ideal when you need to:
- Gather feedback from a large and diverse user group.
- Measure user satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
- Understand user preferences and behaviors related to your product.
- Track changes in user sentiment over time (longitudinal studies).
- Evaluate the effectiveness of design changes or new features.
Real-World Success Stories:
Giants like Apple, Google, and Airbnb leverage the power of surveys and questionnaires. Apple uses the Net Promoter Score (NPS) to gauge customer satisfaction, while Google employs the System Usability Scale (SUS) for product evaluation. Airbnb gathers valuable feedback through post-stay experience surveys, and Mailchimp tracks feature satisfaction with targeted questionnaires. These examples highlight the versatility and impact of this UX research method.
Actionable Tips for Effective Surveys:
- Brevity is Key: Keep surveys focused and concise to minimize survey fatigue and maximize completion rates.
- Clarity Above All: Test your questions beforehand to ensure they are clear, unambiguous, and easy to understand.
- Engage with Variety: Mix different question types (multiple-choice, Likert scales, open-ended) to keep respondents engaged.
- Consistency is Crucial: Use clear scales and consistent formatting throughout the survey.
- Qualitative Gold: Include open-ended questions to uncover deeper insights and understand the "why" behind user responses.
- Incentivize Participation: Consider offering small incentives to boost response rates.
- Start Softly: Begin with engaging, non-threatening questions to build rapport with respondents.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Efficient data collection from large samples
- Statistical validity with proper sampling
- Relatively low cost per respondent
- Easy to repeat for longitudinal studies
- Wide reach across geographically dispersed users
- Quick analysis with the right tools
Cons:
- Potential discrepancy between self-reported data and actual behavior
- Question wording can influence responses
- Survey fatigue can lead to low completion rates
- Limited depth compared to qualitative methods like user interviews
- Potential selection bias in voluntary response samples
- Difficulty probing for deeper insights
For those looking to delve deeper into the practical application of surveys, particularly in the mobile app context, learn more about Surveys and Questionnaires. This resource provides valuable insights into the top mobile feedback tools and how they can be used to gather in-app survey data.
By effectively utilizing surveys and questionnaires as a user experience testing method, you can gain a crucial understanding of your users, identify pain points, and ultimately create products that truly resonate with your target audience. This method empowers you to make data-backed decisions, optimize the user experience, and drive meaningful results for your business.
7. Heatmaps and Session Recordings: Uncover Hidden UX Treasures
Heatmaps and session recordings are powerful user experience testing methods that provide invaluable insights into how users actually interact with your website or application. Unlike traditional user testing methods that rely on observation and interviews, heatmaps and session recordings offer a direct window into user behavior in their natural environment, making them indispensable tools for optimizing the user experience. This approach deserves its place in any UX testing toolkit because it allows for data-driven decision-making based on real user interactions, not just assumptions.
How They Work:
These behavioral analytics tools visualize user interactions with your digital interfaces. Heatmaps aggregate interactions like clicks, taps, and scrolling into color-coded visualizations, revealing engagement patterns and highlighting popular areas. Think of it like a thermal image of your website, where "hot" areas represent high interaction and "cold" areas indicate low engagement. Complementing heatmaps, session recordings capture individual user sessions as video-like playbacks, allowing you to witness real user journeys through your site or application, including mouse movements, clicks, and form interactions.
Features and Benefits:
- Click/Tap Heatmaps: Pinpoint interaction hotspots, revealing which elements users are engaging with most.
- Scroll Maps: Visualize how far users scroll down a page, identifying content visibility and drop-off points.
- Move/Hover Maps: Track cursor movement, showing areas of interest and potential confusion.
- Full Session Recordings: Replay user sessions to understand their navigation flow and identify pain points.
- Form Analytics: Optimize conversion rates by analyzing user behavior within forms, identifying areas of friction.
- Non-Intrusive Data Collection: Gather valuable behavioral data without interrupting the user experience.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- HubSpot: Leveraged heatmaps to optimize conversion paths, improving lead generation and sales.
- The BBC: Utilized scroll maps to analyze content engagement, informing content strategy and layout decisions.
- Shopify: Improved their checkout funnel by using session recordings to identify and address user drop-off points.
- Etsy: Optimized product pages through click tracking and heatmaps, enhancing product discoverability and sales.
When and Why to Use Heatmaps and Session Recordings:
This method is particularly useful for:
- Identifying usability issues: Discover where users struggle to navigate, complete tasks, or find information.
- Optimizing conversion rates: Analyze user behavior in key conversion funnels (e.g., checkout process) to improve performance.
- Evaluating content engagement: Understand how users consume content and identify areas for improvement.
- A/B testing: Compare user behavior on different versions of a page or feature to determine which performs better.
Pros:
- Captures actual user behavior in natural environments.
- Provides visual evidence of user pain points.
- No recruitment or moderation needed.
- Large sample sizes possible.
- Helps prioritize areas for improvement.
- Complements other testing methods with behavioral data.
Cons:
- Lacks context about user intentions or satisfaction.
- Privacy concerns with recording user sessions (addressable with anonymization and clear consent).
- Can generate overwhelming amounts of data (addressable with proper segmentation and filtering).
- May slow down site performance if implemented poorly (choose a reputable provider with minimal impact).
- Requires careful interpretation to avoid false conclusions.
- Generally limited to existing designs, not prototypes.
Actionable Tips:
- Segment your data: Analyze behavior by user types, devices, or traffic sources for more targeted insights.
- Look for patterns: Identify trends across multiple user sessions to gain a holistic understanding of user behavior.
- Set up heatmaps for specific user journeys or conversion paths: Focus your analysis on key areas of interest.
- Combine with analytics data for context: Integrate heatmap and session recording data with other analytics platforms for a comprehensive view.
- Consider consent and privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA): Ensure compliance by obtaining user consent and anonymizing sensitive data.
- Use alongside qualitative methods to understand the 'why': Combine with user interviews or surveys to gain deeper insights into user motivations and frustrations.
Popularized By: Hotjar, Crazy Egg, FullStory, Mouseflow
By incorporating heatmaps and session recordings into your user experience testing strategy, you gain a competitive edge by understanding your users better, identifying hidden pain points, and optimizing your digital products for maximum impact and conversion. This data-driven approach empowers you to make informed decisions based on real user behavior, ultimately leading to a superior user experience and improved business outcomes.
User Experience Testing Methods Comparison
| Method | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usability Testing | Moderate – requires planning, skilled facilitators | Medium – facilities, participants, observers | High – identifies usability issues with qualitative and quantitative data | Early and late-stage product development, task flows | Direct user insights, behavioral & attitudinal data |
| A/B Testing | Moderate to High – needs infrastructure for traffic split and stats | Low to Medium – software tools, sufficient users | High – quantitative validation of design choices, conversion optimization | Optimizing specific elements, validating assumptions | Data-driven, scalable, risk reduction |
| User Interviews | Moderate – interviewer skill needed, scheduling required | Low to Medium – interviewer time, recording tools | High – rich qualitative insights, user motivations and pain points | Exploring user needs, detailed feedback gathering | Empathy building, flexible, uncovers unexpected insights |
| Eye Tracking | High – specialized equipment and technical expertise | High – hardware, setup, calibration | Medium to High – objective visual attention data, subconscious behavior | Visual design optimization, attention studies | Objective, reveals unconscious patterns, visual data |
| Card Sorting | Low to Moderate – preparation and analysis can be simple | Low – participants, cards/tools | Medium – insights into user mental models and info architecture | Information architecture, content structuring | User-driven categorization, quick and inexpensive |
| Surveys and Questionnaires | Low – easy deployment via tools, requires design effort | Low – survey platforms, broad user base | Medium – statistical data on attitudes, satisfaction, demographics | Large-scale feedback collection, tracking satisfaction | Efficient large samples, repeatable, quantitative |
| Heatmaps & Session Recordings | Low to Moderate – implement tracking scripts, manage data | Low to Medium – tracking software, server capacity | Medium – visual and behavioral data on user interaction | Analyzing real user behavior, identifying pain points | Non-intrusive, large scale, behavioral insight |
Elevate Your UX: Putting it All Together
Mastering user experience testing methods is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. From usability testing and A/B testing to the nuanced insights gleaned from eye tracking and card sorting, each method discussed in this article offers a unique lens into the user's mind. By weaving these techniques together, you create a powerful tapestry of understanding, revealing pain points, uncovering hidden opportunities, and ultimately, crafting digital experiences that resonate deeply with your target audience. Remember, the insights you gain from user experience testing methods directly translate to improved conversion rates, stronger customer loyalty, and a more robust bottom line.
The most important takeaway? Don't rely on guesswork. Data-driven decisions fueled by user feedback are the cornerstone of exceptional UX. Whether you're a product manager, marketer, developer, or founder, embracing these methodologies empowers you to build products and services that truly meet the needs of your users. Streamlining operations and optimizing workflows is key to successful implementation. For further exploration on how automation can enhance various aspects of your business, including lead generation and potentially user experience testing, consider these resources: AI strategies that scale results from Fluar’s article on automating lead generation for growth.
Imagine a world where every click, every scroll, every interaction on your platform is seamless and intuitive. That's the power of effective user experience. Ready to transform your UX and unlock its full potential? Start leveraging these user experience testing methods today and witness the remarkable impact on your product and your business. Streamline your user experience testing and efficiently manage feedback with BugSmash, a powerful tool designed to help you gather, organize, and address user feedback throughout the testing process. Start your free trial today and discover how BugSmash can revolutionize your UX workflow.




